It is becoming very common knowledge that web service providers such as Google are penalizing sites that don’t use SSL. Even web browser companies such as Mozilla have started alerting users more actively when they visit sites that don’t have these certificates.
What exactly are these SSL certificates? Why are they so vital that their use is practically enforced? In a nutshell, an SSL certificate helps to make sure the website is safe for browsing. They are the digital identity cards that prove that websites are irrefutably who they say they are.
The SSL protocol is what acts as a secure bridge between the website and a browser. And, the SSL certificate acting as the key to unlock the door. This protects anything which passes between browser and website, making sure your data is safe.
If you’re not convinced, think about the times when you’ve logged on to online banking portals, or even accessed your email account. The SSL connection is a vital portion of what ensures your online privacy and the safety of your information there as well.
If you don’t have an SSL certificate for your website today, there is basically no assurance of data security.
Consumers today are also being rapidly educated regarding online security, so if you don’t catch up quickly, you might lose visitors even if not your search engine standings.
How the SSL Process Works
For the SSL process to work there are two key components needed – the capability to work with the SSL protocol and a valid SSL certificate. On the user end, there is no concern since the design of the web browsers is able to handle SSL protocols.
It is usually on the web server end that needs action to ensure that an SSL certificate is properly obtained and installed. A secure connection is possible once these two conditions met.

When a visitor wants to access a website, the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) sents a request to the web server. This establishes what is known as a handshake. Then what follows is the exchanged of SSL information.
During the process, browser and web server compare notes, so to speak, on important information such as SSL version, compression types and other key parameters. The web server will match the highest level of SSL after such information exchanged. Usually, that is supported by both parties and sends a certificate to the web browser.
From that, the web browser and server can encrypt, and decrypt communications sent between one another. Thus, securing the transmission. The entire process happens quickly and with no user intervention necessary. It is a completely invisible, yet seamless part of the browsing experience.
Types of SSL Available
As with everything involved in the world of security, there are various levels and types you need to know before purchase SSL certificate. These are mainly broken up by the needs of various levels of users.
Domain Validated (DV) Certificates
DV certificates are the most common and easily available. Almost any website can easily obtain one of these. The process only requires that the website owner prove domain ownership and do not even need to provide proof of identity. Unfortunately, because of these lax requirements, there have been multiple cases of websites using them for less than legal purposes.
Organization Validated (OV) Certificates
OV certificates are a small step up. OVs need to validate the one who applies for the certificates has an organization. For example, a company website can apply for an OV certificate since they can prove not only domain ownership and also that they are a valid organization.
Extended Validation (EV) Certificates
EV certificates are even better and have all the benefits of OVs plus more. In the application process, a paper trail is generated which allows anyone to check on the validation process used in obtaining the certificate. If any customers encounter defrauded cases by a site which has an EV certificate, the paper trail can help them seek legal remedies.
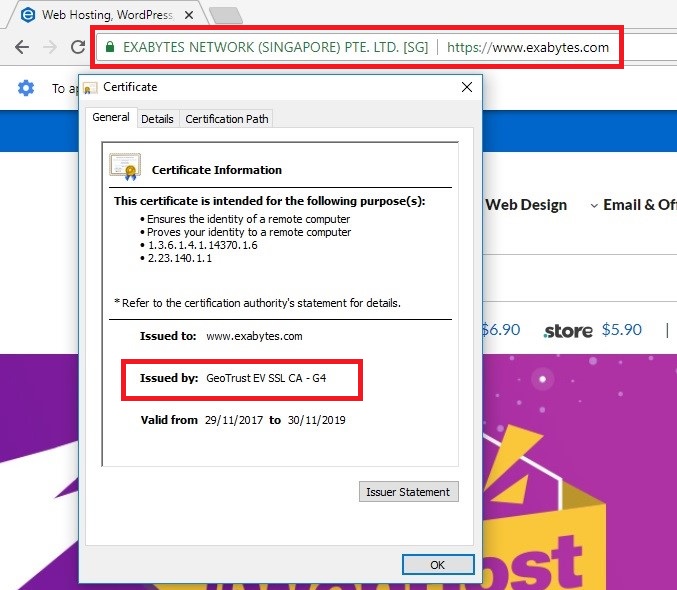
The cost of obtaining one vary greatly. So do shop around before deciding which one you’ll get. For example, some EVs certificates start at around $100, but one from Symantec can cost as much as $995.
Of these three types of certificates, DV is mainly used by personal sites such as blogs. This way, they have a low-cost means of basic assurance to visitors while not having to go through the process (and pay the cost) of an EV or OV certificate. In fact, some corporate websites may opt for them as well. This is especially those which do not manage financial or user details.
When it comes to EV or OV certificates, the extended process means more cost and time needed. As such, they are often only applied for by websites which need to give their users the highest levels of security assurance.
This is especially true of any websites which need to process financial information. Such as an online shopping portal like Amazon.
Where to Get Your SSL Certificate
Because so many websites need SSL now, it has become increasingly easy to find somewhere to obtain one legitimately. From free certificates to commercial ones. They are available through web service providers or even security specialists.

The hosting company such as Exabytes does offer SSL certificates as a part of the hosting security features. You can also get an SSL certificate from security specialists such as Comodo or GlobalSign. Of course, there’s always the option of free SSL such as those from Let’s Encrypt.
The major differences between a paid SSL certificate and a free SSL certificate are often the support, warranty, level of validation and validity period. In terms of security, there’s no difference between both.
After you have purchased an SSL certificate from 3rd party providers, you need to install the certificate to your website manually. The steps for installing the certificate might not as easy as it seems for some people. As such, it’s recommended for beginners to purchase the SSL certificate from your hosting company. As the technical team will help you with the installation.
After you get your SSL certificate, make sure that you double-check with the installation. Ensure you do it correctly. To do this, just visit your website and click on the padlock icon on the address bar.

Just to be sure, it would also be better to use a tool like SSL Shopper which can verify the validity of the certification on your domain. It’s fast and it’s free!
Conclusion
It has only been a relatively recent thing that SSL certification is being forced on website owners. But already, more than half of all sites online have already done so. It is quite a painless process. This is especially for individuals that there really should be no excuse not to have SSL certification.
For those who need better support, OV and EV certificates do cost more, but since they need it to process financial information of their users. I feel that the cost justifiable. Consumers today are becoming increasingly educated, which is a lucky thing since cybercriminals are too.
The potential benefits to your website for using SSL can be great. Also, the penalties for not doing so will hurt. Free is a price that is hard to beat, so if you haven’t already gotten your SSL, do at least check with your web host to see what you can do to obtain one.















